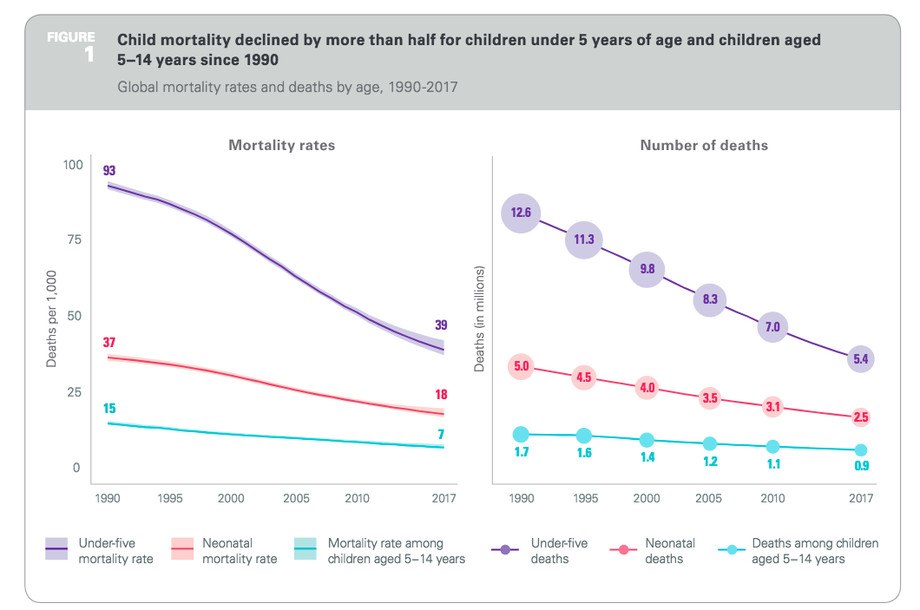
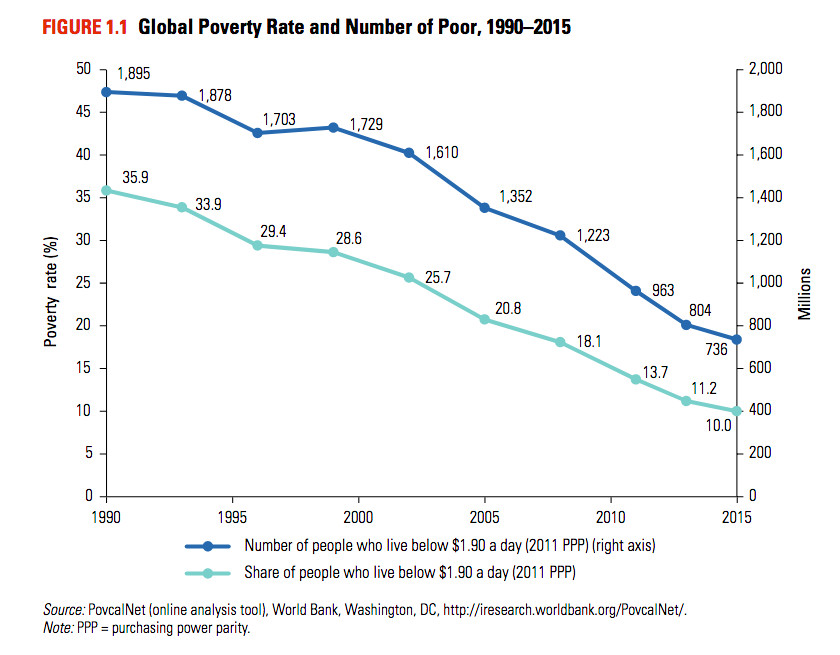
Snow and freezing temperatures endanger flooded refugee camps in Lebanon
Snowstorm “Norma” is battering North Eastern Lebanon with heavy snow, rain and strong winds affecting nearly 250,000 refugees.
Hundreds of refugee camps and settlements in the area from the Akkar Plain to Bekaa Valley have been devastated by the storm. The camps house thousands of Syrian refugees in little more than tents and improvised wooden structures, a number of which have collapsed. UNHCR reported 70% of Syrian refugees in Lebanon live below the poverty line and 41% have precarious and unsafe housing. Some camps have been flooded with as much as half a meter of water, and.
Flooding and heavy rains in Northern Syria, which started on December 26, have also devastated IDP camps across the region. Thousands of tents and the personal possessions of these IDPs were washed away, including medical supplies, wheel chairs and equipment. The people in these camps have lost what little they had left with no way of replacing them.
“Climate change has unleashed hellish conditions on the Syrian refugees in Lebanon. These families are living in tents, with all their clothes and possessions soaked and temperatures below freezing. Children, elderly, the infirm and vulnerable will not survive much longer without being moved to warm and dry locations. This is a humanitarian nightmare and will require an enormous coordinated effort to reach all of these camps in time.” Said Dr. Hussam Al Fakir, Chairman of UOSSM International UOSSM calls on all the international community and NGOs to deploy rapid response teams immediately and upgrade the refugee’s housing to shelters/locations that can adequately handle these harsh conditions.
[Union of Medical Care and Relief Organizations]
Read about the work of Family Care Lebanon who help provide for refugees.